Check out
6 Best High Protein Cereals That Power Your Morning📘 90 Days Plan to Gain Weight
A complete 90-day guide with meal plans, calorie tips, and protein strategies to help you build mass safely and effectively.
⬇️ Download NowThe foundation of any effective mass-building program is a high calorie protein diet. Knowing how to combine enough calories with high-quality protein sources is crucial for anyone trying to gain muscle, recover from illness, or just overcome a stubborn weight plateau. Eating wisely with the proper ratio of nutrients that support growth and recuperation is more difficult than simply increasing one’s food intake.

It takes more than just working out hard to gain muscle. It necessitates a calculated weight-gain diet plan that emphasises high calorie protein diet while preserving nutritional value. By producing the calorie surplus nutrition required for true muscle growth without compromising health or energy levels, the following six tried-and-true methods have assisted innumerable people in changing their bodies.
This thorough guide to mass-building nutrition will teach readers the following:
For the body to create new muscle, it needs enough high calorie protein diets. The building blocks are provided by protein in a high calorie protein diet, while energy for training and recuperation is provided by calories. Age, gender, and degree of activity all affect daily caloric needs, but most people require 300–500 extra calories per day for growth. The idea of calorie surplus versus maintenance is essential because the body cannot produce new tissue without it.
A healthy macronutrient breakdown consists of 0.8-1.2g fats per kg, 4-6g carbs per kg for active people, and 1.6-2.2g protein per kg bodyweight. Because they contain nine calories per gram, healthy fats from foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil are crucial for achieving calorie targets and promoting hormone production.
Warning signs include brittle nails, thinning hair, slow wound healing, persistent muscle weakness, unusual fatigue, and strong cravings for high calorie protein diet. These symptoms should be monitored by anyone on a high calorie protein diet. These signs point to a lack of protein sources and necessitate a quick change in diet.
A complete 90-day guide with meal plans, calorie tips, and protein strategies to help you build mass safely and effectively.
⬇️ Download NowAlthough it is technically possible for excess protein calories to be converted to fat, this process is very inefficient and wastes 25–30% of calories as heat. Protein is the macronutrient that is least likely to result in fat gain in any diet that aims to increase muscle mass because of its high thermic effect (20–30% burned during digestion).
For good reason, this traditional muscle-gain diet has endured over time. It places a strong emphasis on eating frequently, eating whole foods, and timing workouts precisely.
The conventional method concentrates on:
This method, which usually entails five to six meals per day, guarantees that the body always has amino acids on hand for muscle repair. This approach keeps energy levels consistent during training and avoids excessive hunger, which is why many bodybuilders find success with it.
A normal day could consist of:
For serious mass builders, this high calorie protein diet plan offers about 3,500–4,000 calories and more than 200 grammes of protein per day.
The nutrient-dense foods that people consumed prior to modern agriculture are the main focus of the Paleo approach to mass building. It emphasises high-quality meats, vegetables, and natural fats while avoiding processed foods, grains, and dairy.
Paleo critics frequently argue that it restricts calories excessively for mass gain, but thoughtful food selections show otherwise:
The secret is to eat more of the foods that are allowed and to avoid avoiding natural fats. Over 1,000 calories can be easily consumed in one sitting from a large ribeye steak, roasted sweet potatoes, and a generous portion of guacamole.
High calorie protein diets that work well on this plan include:
For people with gastrointestinal sensitivities, this lean mass building diet is perfect because it offers clean calories without the use of refined grains or processed protein powders.
By including substantial amounts of fish, poultry, and legumes along with its characteristic healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet is ideally suited for mass building.
This strategy has special advantages:
Because it doesn’t involve consuming uncomfortable amounts of food, many athletes value this strategy. Olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish have a high calorie density, which makes it easy to reach surplus levels while still eating tasty, diverse meals.
An example of a meal plan could include:
This pattern keeps meals engaging and filling while highlighting high calorie protein diet sources from both plant and animal sources. Without requiring additional food, the extensive use of olive oil during cooking can easily add 300–500 calories per day.
Animal products are not necessary to achieve impressive muscle mass, as demonstrated time and time again by plant-based athletes. This high calorie protein diet depends on careful planning and thoughtful food pairings.
Key high calorie protein diet sources for plant-based mass building include:
The problem with plant-based diets for mass gain is that they contain a lot of fibre, which can make you feel full before you’ve reached your calorie targets. In order to boost calorie density without adding too much volume, successful plant-based bulkers frequently incorporate more processed options like protein powders, nut butters, and meat substitutes.
Some successful strategies are:
By concentrating on achieving particular macronutrient breakdown targets rather than limiting specific foods, “If It Fits Your Macros” (IIFYM) transformed nutrition. It is well-liked by people who want results without feeling deprived because of its adaptability.
Several tenets underpin the IIFYM philosophy:
Because it eliminates the psychological pressure of “perfect” eating, this method is incredibly effective for mass building. As long as they have scheduled their other meals to fit pizza into their daily calorie requirements and macro goals, anyone can enjoy pizza with friends.
For implementation to be successful, the following is necessary:
The majority of IIFYM mass followers strive for:
Strength and endurance-demanding athletes require a unique strategy that supports growth and recovery while fostering intense training. This high calorie protein diet plan places a strong emphasis on quality and timing.
Priorities for performance-focused nutrition include:
Athletes frequently participate in extremely demanding programs or train several times a day. Their daily calorie needs can easily surpass 4,000–5,000, so meal planning and calorie density are crucial. Even one meal missed can result in a deficit that affects recuperation and performance.
A structured approach includes:
The format of an athlete’s sample meal plan could look like this:
This strategy ensures enough fuel for rigorous training regimens while maintaining the calorie surplus vs. maintenance required for growth.
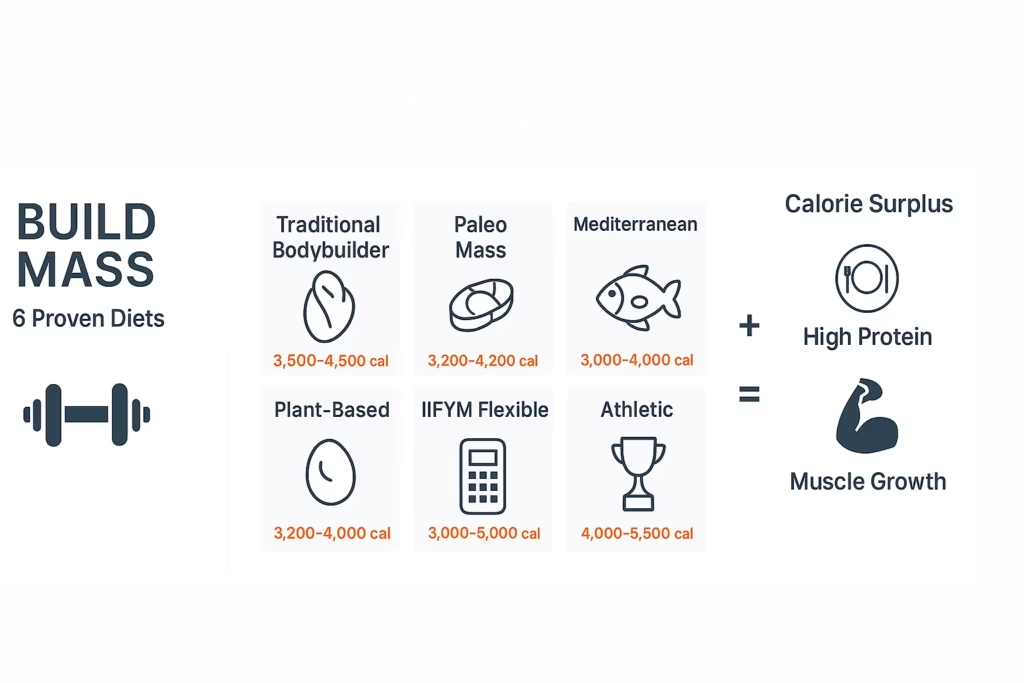
| Diet Approach | Best For | Daily Protein | Daily Calories |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Bodybuilder | Structured lifestyles | 180–250g | 3,500–4,500 |
| Paleo Mass-Gainer | Clean eating, digestive issues | 160–220g | 3,200–4,200 |
| Mediterranean Muscle | Heart health focus | 150–200g | 3,000–4,000 |
| Plant-Based Power | Vegan/vegetarian athletes | 140–200g | 3,200–4,000 |
| Flexible IIFYM | Food freedom seekers | 160–240g | 3,000–5,000+ |
| Athlete’s Performance | High training volume | 180–250g | 4,000–5,500 |
With a high calorie protein diet as the cornerstone, each strategy provides a feasible route to mass gain. Individual preferences, dietary requirements, lifestyle demands, and training objectives all influence the optimal option.
Successful mass-building diets all include some high calorie protein diet, regardless of the exact plan a person follows.
The following are the best protein sources for gaining muscle mass:
Making wise carbohydrate choices is necessary to support calorie surplus nutrition:
A slender person must consistently consume more calories than they expend each day in order to generate a calorie surplus. To make sure that weight gain turns into muscle rather than fat, this entails keeping track of intake, giving calorie-dense protein foods priority, eating more frequently throughout the day, and incorporating strength training. A consistent, healthy weight gain of 0.5–1 pounds per week is usually achieved by beginning with a 300–500 calorie surplus above maintenance levels.
A medium banana has about 1.3 grammes of protein, which is a small amount. Although bananas aren’t a great source of protein, their quick-digesting carbohydrates, potassium content, and convenience make them a good addition to a high-calorie diet. They are great as pre-workout fuel or mixed into protein shakes to provide natural sweetness and calories without using refined sugars.
With only two to three grammes of protein per fruit, avocados are not particularly high in protein. However, because of their calorie density and healthy fats, they are very beneficial in diet plans that aim to build lean mass. About 250–300 calories can be found in one avocado, mostly from healthy monounsaturated fats that promote hormone production and aid in achieving calorie surplus nutrition goals without making you feel bloated.
With about 31 grammes of protein per 100 grammes, chicken breast is the most protein-dense whole food; however, lean beef, turkey, fish, and Greek yoghurt are also excellent choices. Seitan is the best plant-based choice for people who are following plant-based diets because it has up to 75 grammes of protein per 100 grammes. The best protein-rich meals for weight gain are made by combining these protein sources with calorie-dense accompaniments.
Almonds and peanut butter are two of the highest calorie-dense whole foods, with 575 and 590 calories per 100 grammes, respectively, for almonds and peanut butter, respectively. With 884 calories per 100 grammes, oils are even more concentrated, but they don’t contain any protein. Fatty meats like salmon or ribeye steak, when combined with whole eggs, offer excellent calorie-to-protein ratios that are ideal for mass building when it comes to balanced, calorie-dense protein foods.
Scrambled eggs with cheese, Greek yoghurt with granola and nuts, or a protein-rich omelette with veggies and whole grain toast are some examples of high-protein breakfast options. Other good choices are whey powder protein pancakes, cottage cheese with fruit, or a protein powder, oat, nut butter, and milk smoothie. These breakfast options support the meal timing and frequency requirements of a successful weight gain diet plan while offering 30–50 grammes of protein.
It takes dedication to a well-planned, high calorie protein diet that continuously supplies the excess nutrients the body requires for growth to gain noticeable muscle mass. The six tried-and-true methods listed here, which range from conventional bodybuilding to plant-based power, show that there are several ways to get to the same goal. In the end, one’s consistency, level of training intensity, and patience with the process are more important for success than the particular diet they choose.
The best diet for muscle gain is always one that a person can stick to over time while still enjoying the food, having enough energy to train, and seeing steady results. The basic tenets of healthy eating enough protein intake, strategic calorie surplus, high-quality, nutrient-rich foods, and progressive resistance training remain the same regardless of whether an individual favours the structure of traditional meal timing, the food freedom of IIFYM, or the health-focused Mediterranean diet. Anyone can achieve the mass they’ve been aiming for by selecting a strategy that fits their lifestyle and personal preferences.